Scan vulnerabilities of WordPress
Scan WordPress (core, plugin, theme)
For non-commercial use, you can use this WordPress integration for free. But for commercial use, You have to send a E-Mail to the WPScan Team. For Details, see the NOTE:
If you are under any doubt if your software is classed as non-commercial and/or would like to inquire about commercial usage of our databases get in touch.
First, you need to register a user and get the API token from your profile page on wpscan.com. And then, check whether the wp command is installed on the scan target server. A sample configuration is below.
- config.toml
[wpscan]
token = "Token"
detectInactive = false
[servers.kusanagi]
user = "root"
host = "10.10.10.10"
port = "22"
[servers.kusanagi.wordpress]
cmdPath = "/usr/local/bin/wp"
osUser = "wordpress"
docRoot = "/home/kusanagi/wp/DocumentRoot/"
noSudo = false
- token: A token of wpscan.com
- detectInactive : Detect plugins or themes which are inactive state
- cmdPath : A path of
wpon the wordpress server - osUser : A OS user of
wpon the wordpress server - docRoot : A path of document root on the wordpress server
- noSudo : Run the
wpcommand with sudo privileges
Scan
To scan WordPress, execute as below.
$ vuls scan kusanagi
Vuls collects WordPress Core version, plugins and themes via wp-cli.
Reporting
$ vuls report
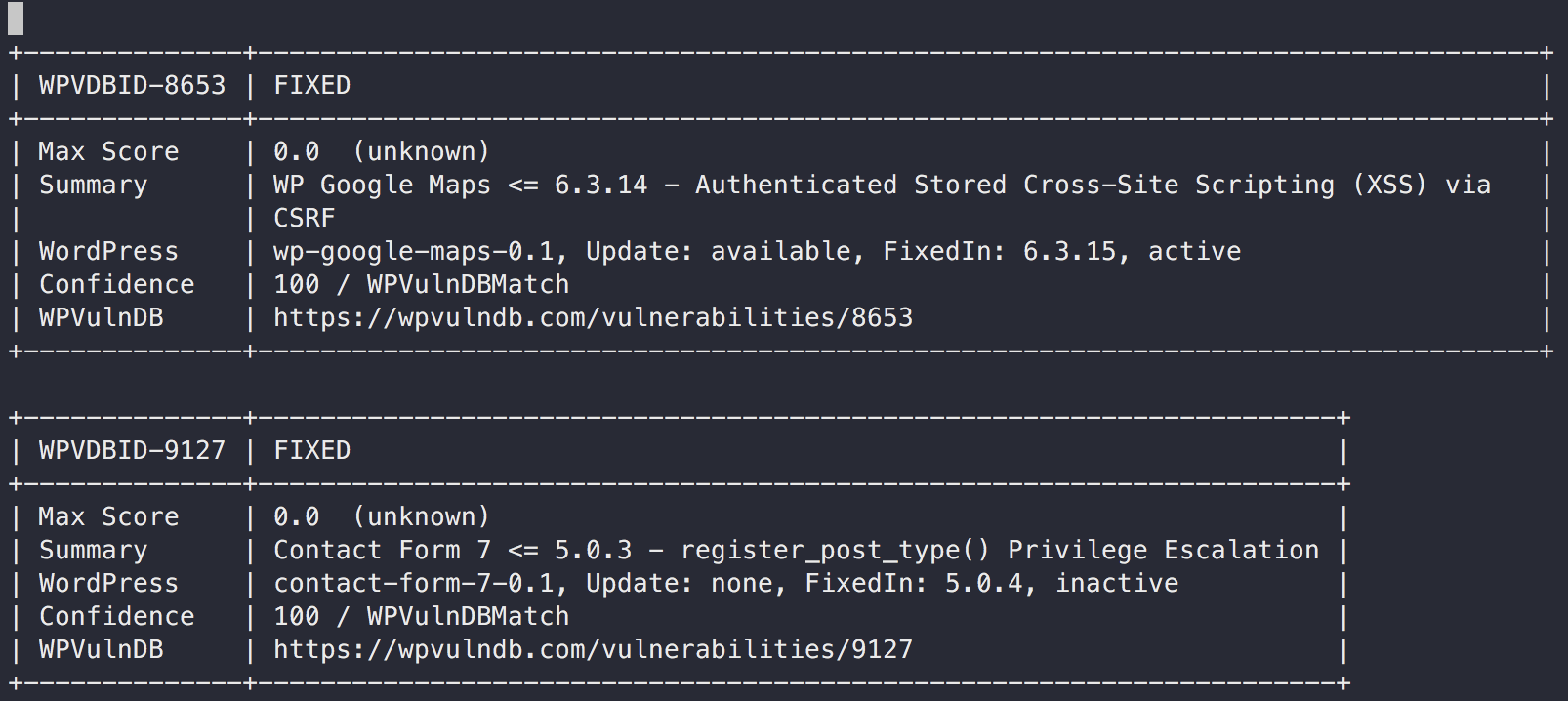
Vuls detects vulnerabilities via accessing WPScan.com via HTTP.
- Slack


- TUI

- Full-Text
Tips
- If you have some virtual WordPress sites in a server.
- If you want a report of only WordPress without OS packages.
# for server administrator
[servers.wordpress]
host = "wordpress"
# for WordPress site FOO
[servers.foo]
host = "wordpress"
scanModules = ["wordpress"]
[servers.foo.wordpress]
docRoot = "/home/foo/wordpress/"
# for WordPress site BAR
[servers.bar]
host = "wordpress"
scanModules = ["wordpress"]
[servers.bar.wordpress]
docRoot = "/home/bar/wordpress/"
If sudo cannot be executed with scan user
Set noSudo = true to execute the command without sudo.
If scan user and wordpress osUser are different, it is necessary to be able to switch from scan user to wordpress osUser without a password, since the command is executed by switching to wordpress osUser.
See PR #1523 if you want to know the actual command to be executed.
For example, the following config requires that the switch from user to wordpress (user $ su - wordpress) can be executed without a password.
[servers.wordpress]
user = "user"
[servers.wordpress.wordpress]
cmdPath = "/usr/local/bin/wp"
osUser = "wordpress"
docRoot = "/var/www/html"
noSudo = true