CPE Scan
Vuls can detect vulnerabilities in network devices and commercial middleware by defining CPE in config.toml. The OS package scan is done by actually SSH into the server and issuing the command. However, the CPE scan is detected by comparing the versions of the NVD and JVN databases. It does not issue commands on the device and does not access the device via a network.
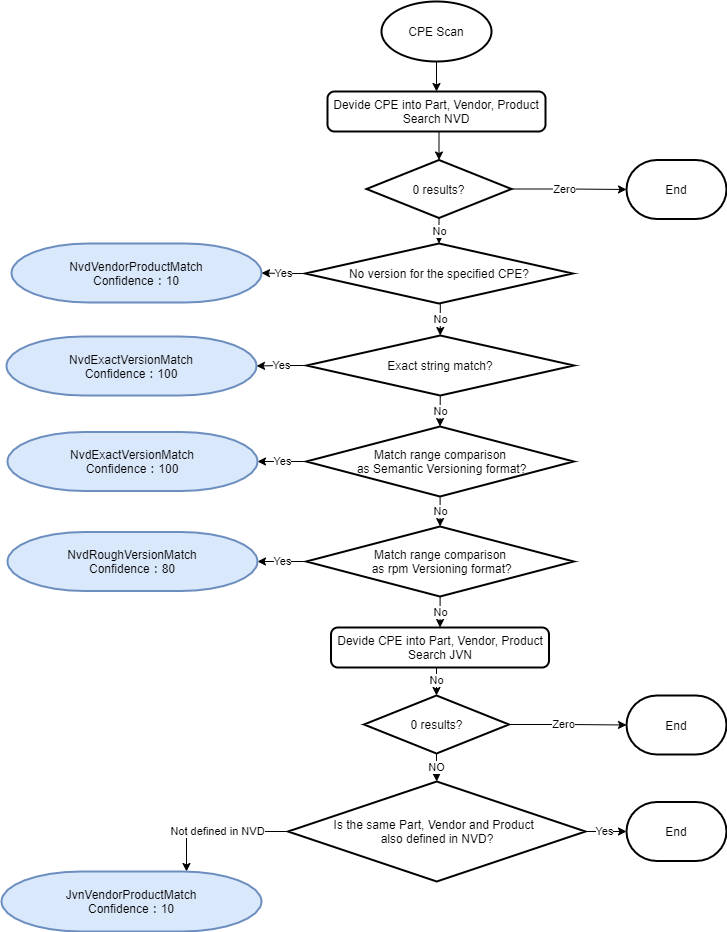
Tutorial: usage-scan-non-os-packages Tutorial: Vulsctl/cpe scan